Program 12:
Build a Rails application to accept book information viz. Accession number, title, authors, edition and publisher from a web page and store the information in a database and to search for a book with the title specified by the user and to display the search results with proper headings.
Procedure for execution:
- Open a terminal and run
mkdir rails_app && cd $_ - Create a new app called books using the command
rails new books -d mysql - Run the command
cd books/configand open the database.yml file to set mysql username and password by running the commandnano database.yml. The username and password are required to be filled at 3 sections in the file. -
The following is a sample snippet from the database.yml file-
adapter: mysql2
encoding: utf8
reconnect: false
database: books_development
pool: 5 username: root
password: pass
socket: /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock -
Save the file by
ctrl+xand theny. - Now run
cd ..and make sure that you are present in therails_app/booksdirectory. - Run the command
rake db:create - Next, run
rails generate controller books index - Next, run
rails generate model book access_no:integer title:string author:string edition:integer publisher:string - Run
rake db:migrate -
Now,
cd app/views/booksand edit the filenano index.html.erb- -
Also, edit the file
nano search.html.erb - Now,
cd ../../controllersand edit the filenano books_controller.rb - Next, run
cd ../../configand editnano routes.rbfile. - Finally, run
cd ..and start the rails server by running the commandrails s - Open a browser and in the address bar type
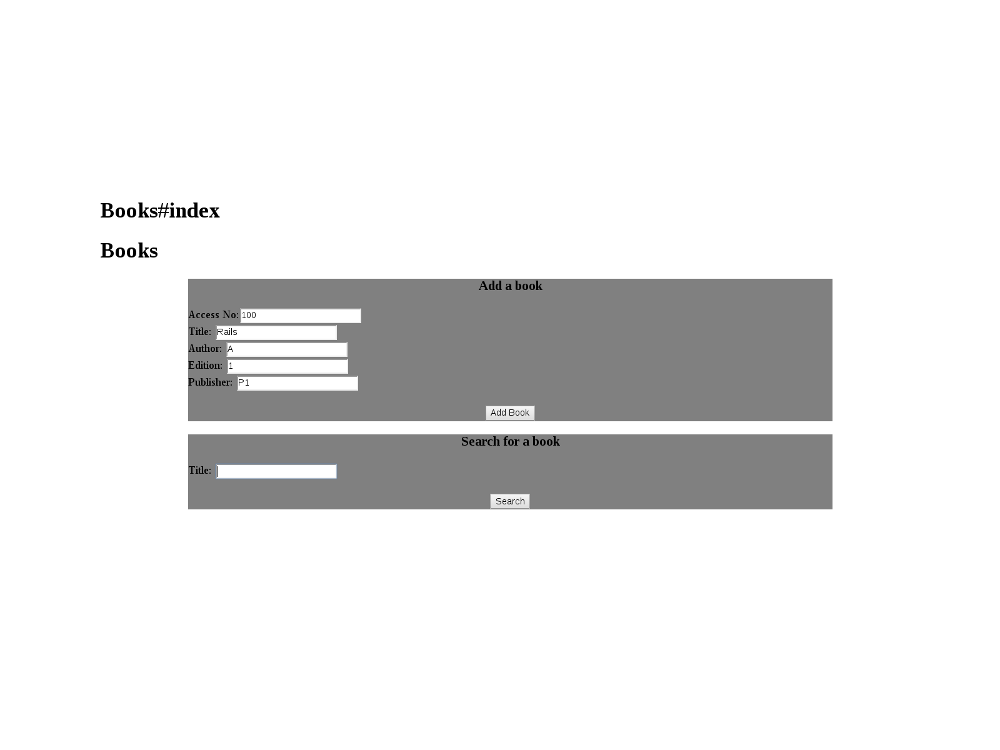
localhost:3000to check if the rails server is running. If yes, add to the URL,localhost:3000/books/index. - Enter the input & on successfully inserting data, search for the same from the browser. The output is displayed in a table on the browser.
Explaination
- The rails new command has created a Rails application in a new directory called books
- The -d options in the rails new command allows us to specify which DBMS to use. The default is sqlite. However we use mysql
- The database.yml file has all the cofiguration information which allows our application to connect, create and modify the database
- You run rake db:create once and only once, and you run it first. Then you run rake db:migrate every time you add/change a migration
- The rails generate controller command created a lot of files and directories. We are interested in two of them for now :-
- app/controllers/books_controller.rb
- app/views/books/index.html.erb
- Inside Rails application, the controller file is placed inside app/controllers directory
-
The Controller
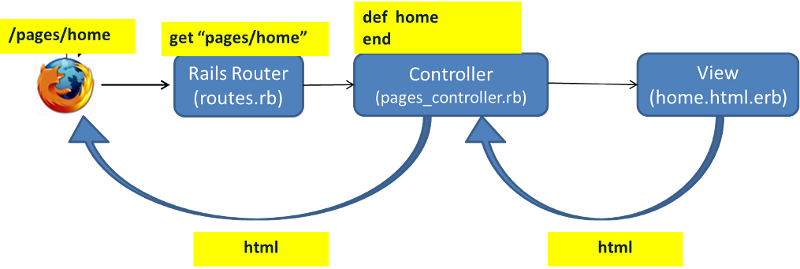
- User types a URL, lets say http://localhost:3000/pages/home. If the Rails server is running, the request first reaches the Rails router.
-
-
The Router checks the config/routes.rb file to see if there is an entry matching the URL requested. In our case there is a route entry - get "pages/home". In short, the route matches incoming URL
/pages/hometo home action in Pages controller. So the request is forwarded to the Pages controller, home action. -
-
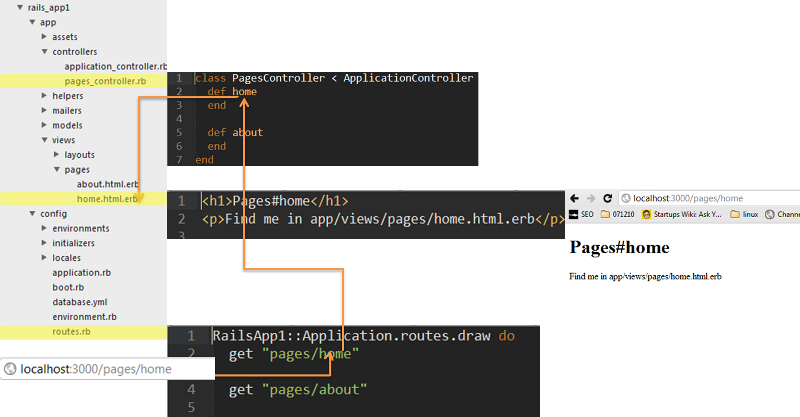
In our program the BooksController is a class. Intially there is an empty method index inside the class. The method is also called index action in the Books controller.
class BooksController < ApplicationController def index end -
This action serves the url /books/index when accessed. Even though the index action is an empty method, it fetches the file /apps/views/books/index.html.erb and displays it on the browser.
-
The Model
- Rails interact with the database through models. In our program we have a model called Book. This ensures that the our model is independent of the DBMS
- When you create a model, the name is singular and the name starts with capital letter. Book, instead of Books
-
In our model we have the following attributes
- access_no:integer
- title:string
- author:string
- edition:integer
- publisher:string
-
The
rails generate modelcommand also creates a migration file present under db/migrate - The migration file is like schema which defines the database table structure
- rake db:migrate pushes the database changes from the migration file to the actual database
-
If you end up doing a mistake you can always undo the creation of a model using
rails destroy model Book -
If you want to delete the database from the DBMS once the model has been migrated use
rake db:rollback-
Ruby Tags
- RoR has the following 2 tags :
- <% %> : The output of this tag will NOT be displayed on the browser
- <%= %> : The output will be displayed on the browser
Code:
- index.html.erb
-
<h1>Books</h1><br>
<h3 style="text-align: center;">Add a book</h3><br>
<%= form_tag("/books/add", :method=>"post") do %>
<form action="/books/add" method="post"> <br>
Access No:<%= text_field_tag(:b_access_no) %>
//create input tags of given type and id
<input type="text" id=":b_access_no"><br>
<br>Title: <%= text_field_tag(:b_title) %>
<input type="text" id=":b_title"><br>
<br>Author: <%= text_field_tag(:b_author) %>
<input type="text" id=":b_author"><br>
<br>Edition: <%= text_field_tag(:b_edition) %>
<input type="text" id=":b_edition"><br>
<br>Publisher: <%= text_field_tag(:b_publisher) %>
<input type="text" id=":b_publisher"><br>
<br><br>
<%= submit_tag("Add Book") %>
<input type="submit" value="Add Book"><br>
<% end %>
<br>
<h3 style="text-align: center;">Search for a book</h3><br>
<%= form_tag("/books/search", :method=>"post") do %>
<form action="/books/search" method="post"><br>
Title: <%= text_field_tag(:bs_title) %>
<input type="text" id=":bs_title"><br>
<br><br>
<%= submit_tag("Search") %>
<input type="submit" value="Search"><br>
<% end %>
<br>
- search.html.erb
<h1>Search Result</h1><br>
<table border=1><br>
<% @t=Book.find_by_title(params[:bs_title]) %>
//RoR creates a find_by_attribute method for our model. In our case we are asked to search by title hence we are using the find_by_title function. This function takes a string as parameter. Here we are using the the value in :bs_title that was passed on using post method when the button was pressed. This function returns an array. Arrays in ruby begin with the '@' symbol
<br>
<tr><br>
<th>Access No.</th><br>
<th>Title</th><br>
<th>Author</th><br>
<th>Edition</th><br>
<th>Publisher</th><br>
</tr><br>
<tr><br>
//Elements of an array are accessed by the "." operator followed by the attribute name.
//In our case we are accessing the access_no that was returned to the array t.
<td> <%= @t.access_no %> </td>
<td> <%= @t.title %> </td>
<td> <%= @t.author %> </td>
<td> <%= @t.edition %> </td>
<td> <%= @t.publisher %> </td>
</tr><br>
</table><br>
<br><br><br>
<a href="/books/index">Back</a>
<br>
- books_controller.rb
class BooksController < ApplicationController
//auto-generated code
def index
//auto-generated code
end
//auto-generated code<br>
def add
//create a new action called add which performs the below action
Book.create(:access_no=>params[:b_access_no],:title=>params[:b_title],:author=>params[:b_author],:edition=> params[:b_edition],:publisher=> params[:b_publisher])
//the create method is used to add a vlaue to the DB. The values to be added are fetched from the post method using the param function
redirect_to :action => 'index'
//once the add button is clicked this specifes which page is to be displayed.Here the index page is redisplayed
end
def search
//defines the search action. Just displayes search.html.erb on browser
end
end
- routes.rb
Books::Application.routes.draw do
//auto generated code
match "books/index" => "books#index", :as => :index
//use the action defined under index when request for /books/index is recieved<br>
match "books/add" => "books#add", :via => :post
//use action defined under add when request for books/add is recieved via post method<br>
match "books/search" => "books#search", :via => :post
//use action defined under search when request for books/search is recieved via post method<br>
Screenshots: