Aim :
Write a C/C++ POSIX compliant program that prints the POSIX defined configuration options supported on any given system using feature test macros.
Theory :
POSIX allows an application to test at compile or run time whether certain options are supported, or what the value is of certain configurable constants or limits.
- _POSIX_SOURCE:If you define this macro, then the functionality from the POSIX.1 standard (IEEE Standard 1003.1) is available, as well as all of the ISO C facilities.
- _POSIX_C_SOURCE:Define this macro to a positive integer to control which POSIX functionality is made available. The greater the value of this macro, the more functionality is made available.
- _POSIX_JOB_CONTROL:If this symbol is defined, it indicates that the system supports job control. Otherwise, the implementation behaves as if all processes within a session belong to a single process group. See section Job Control.
- _POSIX_SAVED_IDS:If this symbol is defined, it indicates that the system remembers the effective user and group IDs of a process before it executes an executable file with the set-user-ID or set-group-ID bits set, and that explicitly changing the effective user or group IDs back to these values is permitted. If this option is not defined, then if a nonprivileged process changes its effective user or group ID to the real user or group ID of the process, it can't change it back again.
- _POSIX_CHOWN_RESTRICTED:If this option is in effect, the chown function is restricted so that the only changes permitted to nonprivileged processes is to change the group owner of a file to either be the effective group ID of the process, or one of its supplementary group IDs.
- int _POSIX_NO_TRUNC:If this option is in effect, file name components longer than NAME_MAX generate an ENAMETOOLONG error. Otherwise, file name components that are too long are silently truncated.
- _POSIX_VDISABLE:This option is only meaningful for files that are terminal devices. If it is enabled, then handling for special control characters can be disabled individually.
Code:
#define _POSIX_SOURCE
#define _POSIX_C_SOURCE 199309L
#include "iostream"
#include<unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
#ifdef _POSIX_JOB_CONTROL
cout<<"System supports POSIX job control:"<<_POSIX_JOB_CONTROL<<endl;
#else
cout<<"System does not support POSIX job control"<<endl;
#endif
#ifdef _POSIX_SAVED_IDS
cout<<"System supports saved set UID and GID:"<<_POSIX_SAVED_IDS<<endl;
#else
cout<<"System does not support saved set GID and UID"<<endl;
#endif
#ifdef _POSIX_CHOWN_RESTRICTED
cout<<"Chown restricted option is :"<<_POSIX_CHOWN_RESTRICTED<<endl;
#else
cout<<"Chown Restricted not defined"<<endl;
#endif
#ifdef _POSIX_NO_TRUNC
cout<<"Truncation option is :"<<_POSIX_NO_TRUNC<<endl;
#else
cout<<"Truncation Option not defined"<<endl;
#endif
#ifdef _POSIX_VDISABLE
cout<<"disable char for terminal files"<<_POSIX_VDISABLE<<endl;
#else
cout<<"char for terminal device files will not be diasbled"<<endl;
#endif
return 0;
}
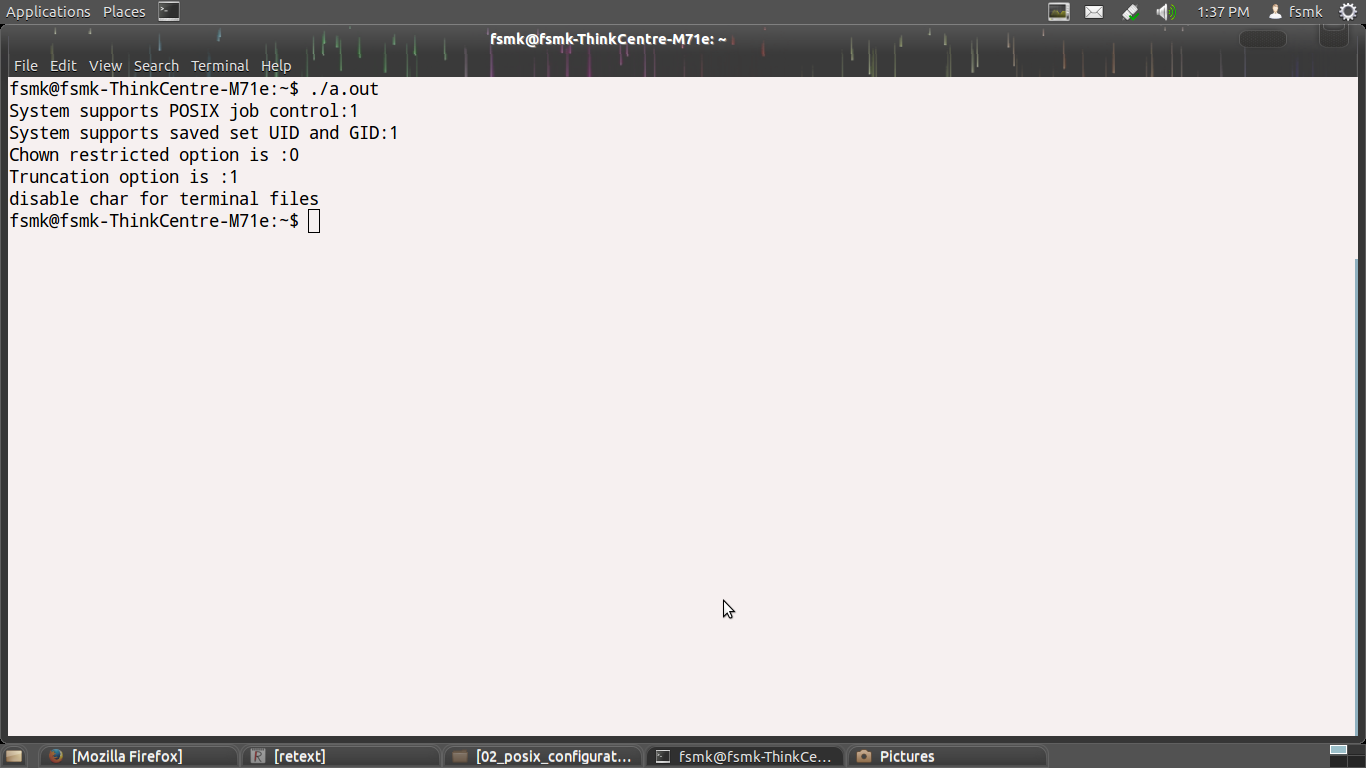
Output:
- Open a terminal.
- Change directory to the file location in the terminals.
- Open a file using command followed by program_name
- Then compile the program using
- If there are no errors after compilation execute the program using
vi 02_posix_configuration.cppand then enter the source code and save it.
g++ 02_posix_configuration.cpp
./a.out
Screenshots: