Aim:
Write a program for simple RSA algorithm to encrypt and decrypt the data.
Description:
Cryptography has a long and colorful history. The message to be encrypted, known as the plaintext, are transformed by a function that is parameterized by a key. The output of the encryption process, known as the ciphertext, is then transmitted, often by messenger or radio. The enemy, or intruder, hears and accurately copies down the complete ciphertext. However, unlike the intended recipient, he does not know the decryption key and so cannot decrypt the ciphertext easily. The art of breaking ciphers is called cryptanalysis the art of devising ciphers (cryptography) and breaking them (cryptanalysis) is collectively known as cryptology.
There are several ways of classifying cryptographic algorithms. They are generally categorized based on the number of keys that are employed for encryption and decryption, and further defined by their application and use. The three types of algorithms are as follows:
- Secret Key Cryptography (SKC): Uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. It is also known as symmetric cryptography.
- Public Key Cryptography (PKC): Uses one key for encryption and another for decryption. It is also known as asymmetric cryptography.
- Hash Functions: Uses a mathematical transformation to irreversibly "encrypt" information Public-key cryptography has been said to be the most significant new development in cryptography. Modern PKC was first described publicly by Stanford University professor Martin Hellman and graduate student Whitfield Diffie in 1976. Their paper described a two-key cryptosystem in which two parties could engage in a secure communication over a non-secure communications channel without having to share a secret key.
Generic PKC employs two keys that are mathematically related although knowledge of one key does not allow someone to easily determine the othe r key. One key is used to encrypt the plaintext and the other key is used to decrypt the ciphertext. The important point here is that it does not matter which key is applied first, but that both keys are required for the process to work. Because pair of keys is required, this approach is also called asymmetric cryptography.
In PKC, one of the keys is designated the public key and may be advertised as widely as the owner wants. The other key is designated the private key and is never revealed to another party. It is straight forward to send messages under this scheme. The RSA algorithm is named after Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Len Adleman, who invented it in 1977.
The RSA algorithm can be used for both public key encryption and digital signatures. Its security is based on the difficulty of factoring large integers.
Algorithm:
- Generate two large random primes, P and Q, of approximately equal size.
- Compute N=PxQ
- Compute Z=(P-1) x (Q-1).
- Choose an integer E, 1<E<Z, such that GCD (E, Z) = 1
- Compute the secret exponent D, 1<D<Z, such that ExD ≡ 1(mod Z)
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
long int gcd(long int a, long int b)
{
if(a == 0)
return b;
if(b == 0)
return a;
return gcd(b, a%b);
}
long int isprime(long int a)
{
int i;
for(i = 2; i < a; i++){
if((a % i) == 0)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
long int encrypt(char ch, long int n, long int e)
{
int i;
long int temp = ch;
for(i = 1; i < e; i++)
temp = (temp * ch) % n;
return temp;
}
char decrypt(long int ch, long int n, long int d)
{
int i;
long int temp = ch;
for(i = 1; i < d; i++)
ch =(temp * ch) % n;
return ch;
}
int main()
{
long int i, len;
long int p, q, n, phi, e, d, cipher[50];
char text[50];
cout << "Enter the text to be encrypted: ";
cin.getline(text, sizeof(text));
len = strlen(text);
do {
p = rand() % 30;
} while (!isprime(p));
do {
q = rand() % 30;
} while (!isprime(q));
n = p * q;
phi = (p - 1) * (q - 1);
do {
e = rand() % phi;
} while (gcd(phi, e) != 1);
do {
d = rand() % phi;
} while (((d * e) % phi) != 1);
cout << "Two prime numbers (p and q) are: " << p << " and " << q << endl;
cout << "n(p * q) = " << p << " * " << q << " = " << p*q << endl;
cout << "(p - 1) * (q - 1) = "<< phi << endl;
cout << "Public key (n, e): (" << n << ", " << e << ")\n";
cout << "Private key (n, d): (" << n << ", " << d << ")\n";
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
cipher[i] = encrypt(text[i], n, e);
cout << "Encrypted message: ";
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
cout << cipher[i];
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
text[i] = decrypt(cipher[i], n, d);
cout << endl;
cout << "Decrypted message: ";
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
cout << text[i];
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
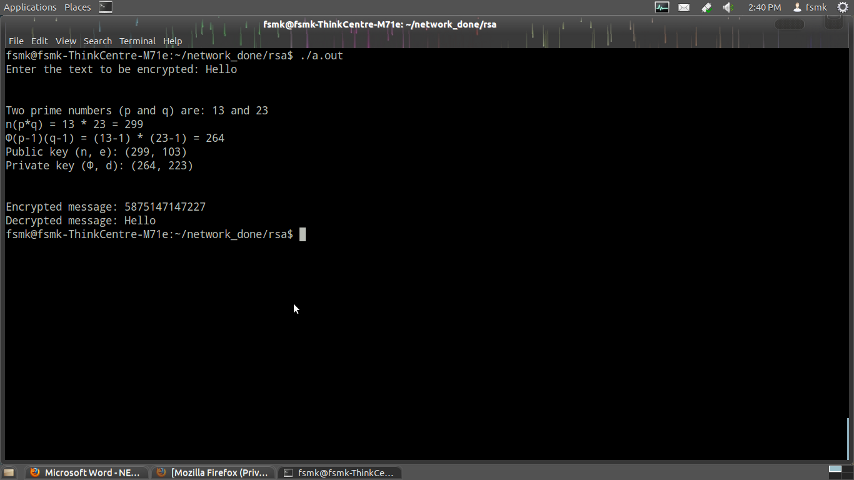
Output:
Commands for execution:-
- Open a terminal.
- Change directory to the file location.
- Run g++ filename.cpp
- If there are no errors, run ./a.out
Screenshots:-