Name of the Program:
Design, develop, and execute a program in C++ to create a class called LIST (linked list) with member functions to insert an element at the front of the list as well as to delete an element from the front of the list. Demonstrate all the functions after creating a list object.
Theory:
In computer science, a linked list is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence. Under the simplest form, each node is composed of a datum and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence; more complex variants add additional links. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence.
A linked list whose nodes contain two fields: an integer value and a link to the next node. The last node is linked to a terminator used to signify the end of the list.
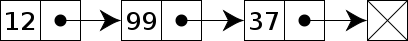
Linked lists are among the simplest and most common data structures. They can be used to implement several other common abstract data types, including lists (the abstract data type), stacks, queues, associative arrays, and S-expressions, though it is not uncommon to implement the other data structures directly without using a list as the basis of implementation.
The principal benefit of a linked list over a conventional array is that the list elements can easily be inserted or removed without reallocation or reorganization of the entire structure because the data items need not be stored contiguously in memory or on disk. Linked lists allow insertion and removal of nodes at any point in the list, and can do so with a constant number of operations if the link previous to the link being added or removed is maintained during list traversal.
On the other hand, simple linked lists by themselves do not allow random access to the data, or any form of efficient indexing. Thus, many basic operations - such as obtaining the last node of the list (assuming that the last node is not maintained as separate node reference in the list structure), or finding a node that contains a given datum, or locating the place where a new node should be inserted - may require scanning most or all of the list elements.
Algorithm:
- Create a class by name "list" having data members info and a link.
- Member methods are insfrnt(), delfrnt() and display().
- insfrnt() method adds a new node to the front of the list and assigns the data to it.
- delfrnt() checks if the list is empty if not then the first node from the list is deleted.
- display() displays the whole list by traversing through the list.
- A class list is created with data members info,link and methods insfrnt(),delfrnt() and display().
Code:
list.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
class list
{
int info;
list *link;
public:
void insfrnt();
int delfrnt();
void display();
}*header;
int main()
{
int a;
list obj;
while(1)
{
cout<<"\nEnter your choice\n1-Insert at front\n2-Delete at front\n3-Display\nAnyother to exit\n";
cin>>a;
switch(a)
{
case 1:obj.insfrnt();break;
case 2:obj.delfrnt();break;
case 3:obj.display();break;
default:exit(0);
}
}
return 0;
}
void list::insfrnt()
{
list *temp;
int x;
temp=new list;
temp->link=NULL;
cout<<"Enter the value of info:";
cin>>x;
temp->info=x;
if(header==NULL)
header=temp;
else
{
temp->link=header;
header=temp;
}
}
int list::delfrnt()
{
if(header==NULL)
cout<<"Empty list";
else
{
list *temp;
temp=header;
cout<<temp->info;
header=header->link;
free(temp);
}
}
void list::display()
{
list *temp;
if(header==NULL)
cout<<"Empty list";
else
{
for(temp=header;temp!=NULL;temp=temp->link)
cout<<temp->info<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
}
}
Steps for obtaining output:
Steps for checking output-
- Locate the folder in which the file is present in the terminal.
- Execute the command "gcc the
" - Execute ethe command "./a.out"
Output:
Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:1 Enter the element to be inserted:12 Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:1 Enter the element to be inserted:23 Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:1 Enter the element to be inserted:34 Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:1 Enter the element to be inserted:45 Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:3 The elements of the list are... 45->34->23->12->NULL Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:2 The deleted element = 45 Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:2 The deleted element = 34 Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:3 The elements of the list are... 23->12->NULL Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:2 The deleted element = 23 Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:3 The elements of the list are... 12->NULL Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:2 The deleted element = 12 Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:3 The list is empty Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:2 The list is empty Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:4 Enter the choice of operation: 1.Insert 2.Delete 3.Display 4.Exit:4
Screenshots:
